Critical Critters
Science Challenge
Jump to...
Email us for the Teacher's Guide!
DAY 1
Keystone Species
Keystone species are plants, animals, or fungi that have an incredibly large impact on their ecosystem, even though they may have a small population. They are one of the most important organisms in their environment. If we removed keystone species from their ecosystem, the ecosystem would likely fall apart.
Even though some keystone species may be small or have small populations, they keep the ecosystem balanced. Without them, a domino effect would occur and cause the ecosystem to collapse.
Predators, mutualists (animals that interact and benefit each other), and ecosystem engineers are often considered keystone species because of their impact on other species and the environment.
Keystone Species Examples
Alligators
Alligators are important predators and help to keep populations of fish in check. They prevent the spread of disease by eating dead animals and dig "gator holes" that collect water that other animals will drink during droughts.
Bees
Small but mighty, bees are important pollinators. Without bees, plants would not be pollinated and would not be able to reproduce. This would affect every animal that depends on plants for food or shelter.
Wolves
Wolves help to keep species of deer and other herbivores in check by being successful predators. Without wolves, the populations of grazers would increase and overgraze the landscape, which would change the ecosystem.
Keystone Catastrophe
For each keystone species below, make a hypothesis to explain what would happen if the animal became extinct from the ecosystem. Click the dropdown arrow to check your work.
- 1. In kelp forest ecosystems, sea urchins aggressively feed on kelp and are kept in check by sea otter predation. What would happen if SEA OTTERS disappeared?
If sea otters disappeared, the sea urchin population would grow because they would have fewer predators. As the sea urchin population grew, they would eat more and more kelp. As the kelp disappeared, fewer marine animals would be found in that area because their shelter is gone.
- 2. In the Sonoran Desert, saguaro cacti provide nesting spots to many species of birds and, when they die, they create shelter for invertebrates. What would happen if saguaro cacti disappeared?
If saguaros disappeared, fewer birds would have places to nest and their populations would either shrink or disperse to new areas. Invertebrates and small mammals that live in the fallen cacti would have to find shelter elsewhere or be more vulnerable to predation and extreme temperatures.
- 3. Hummingbirds are important cactus pollinators, especially in areas where there are invasive grasses! What would happen if hummingbirds disappeared?
If hummingbirds disappeared, native cacti would not get pollinated and would not be able to produce fertile seeds. As the cactus population shrinks, invasive grasses would have more room and resources to take over the landscape.
- 4. Sea stars are keystone species in tidepools where they feed on mussels and algae-eating animals. What would happen if sea stars disappeared?
If sea stars disappeared, populations of mussels and other algae-eating animals would grow and begin to compete with each other for food and resources. This would eventually deplete the tidepool of all of its nutrients.
- 5. Mountain lions prey on many species such as deer and rabbits; many species avoid living near them. They often leave many leftovers that vultures feed on. What would happen if mountain lions disappeared?
If mountain lions disappeared, populations of deer and rabbits would grow, travel to new areas, and overgraze the landscape. This would eventually make it challenging for herbivores to find food and drive them out of the ecosystem.
Challenge #1
The video below demonstrates the incredible impact keystone species have, not only on other species but on the landscape as a whole.
For challenge #1, watch "How Wolves Change Rivers" and write 1-2 paragraphs describing how removing wolves from the landscape impacted the entire ecosystem.
DAY 2
Ecosystem Engineer
Ecosystem engineers are organisms who significantly modify their ecosystem. They are responsible for either maintaining, destroying, or creating habitats or resources within their ecosystem.
Many animals change their ecosystems. In fact, some scientists would argue that every animal changes its ecosystem in some way! From pollinating bees that create lush landscapes to herbivorous rabbits that eat young trees and prevent the growth of forests, all animals contribute to the balance of their ecosystem. Ecosystem engineers, however, have a HUGE contribution!
Ecosystem engineers often change the landscape by performing tasks that help them survive, like knocking trees down for food, digging holes for water, or creating structures to live in. These actions, unknowingly to the engineer, will often benefit many other species in the ecosystem! Ecosystem engineers often practice commensalism, where they benefit another species while being unaffected by that other species.
Engineering Endeavor
Below are four pictures of how ecosystems have been impacted by ecosystem engineers. For each photo, identify which ecosystem engineer modified that ecosystem! Click the drop-down arrow to check your work.
- Answer
D - Woodpeckers
Woodpeckers create holes in trees, telephone poles, and other structures while they search for bugs. These holes are then used by other birds for nesting spots.
- Answer
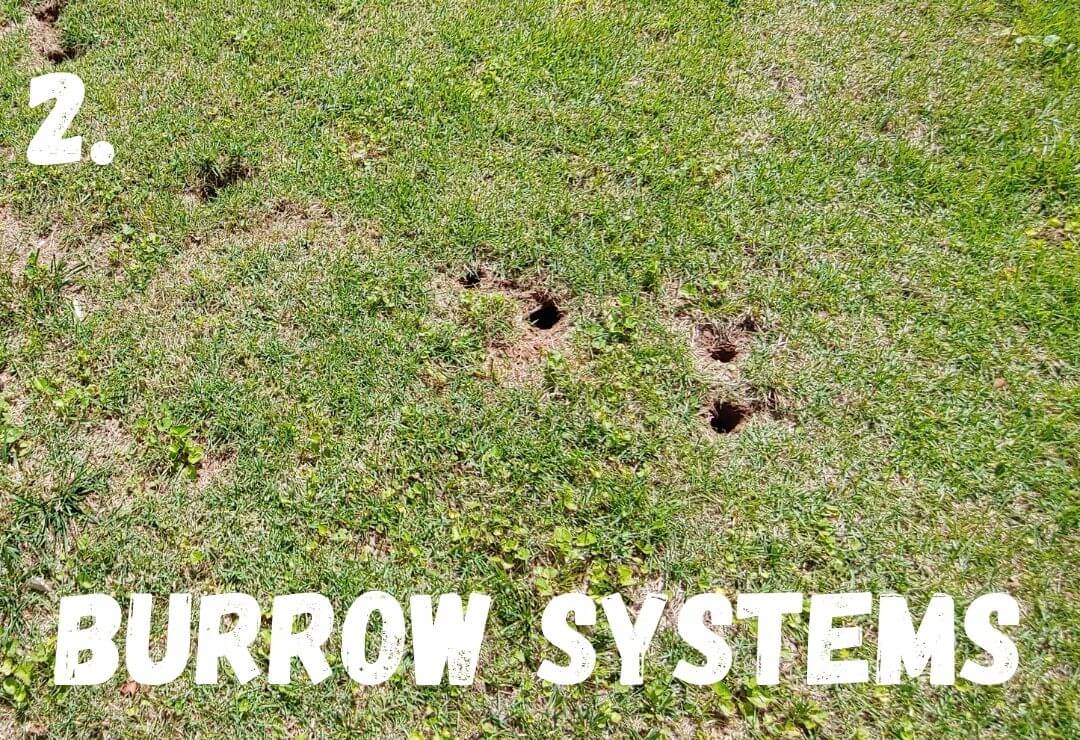
A - Prairie Dog
Prairie dogs make intricate burrow systems that help aerate the soil and create shelters for other animals!
- Answer
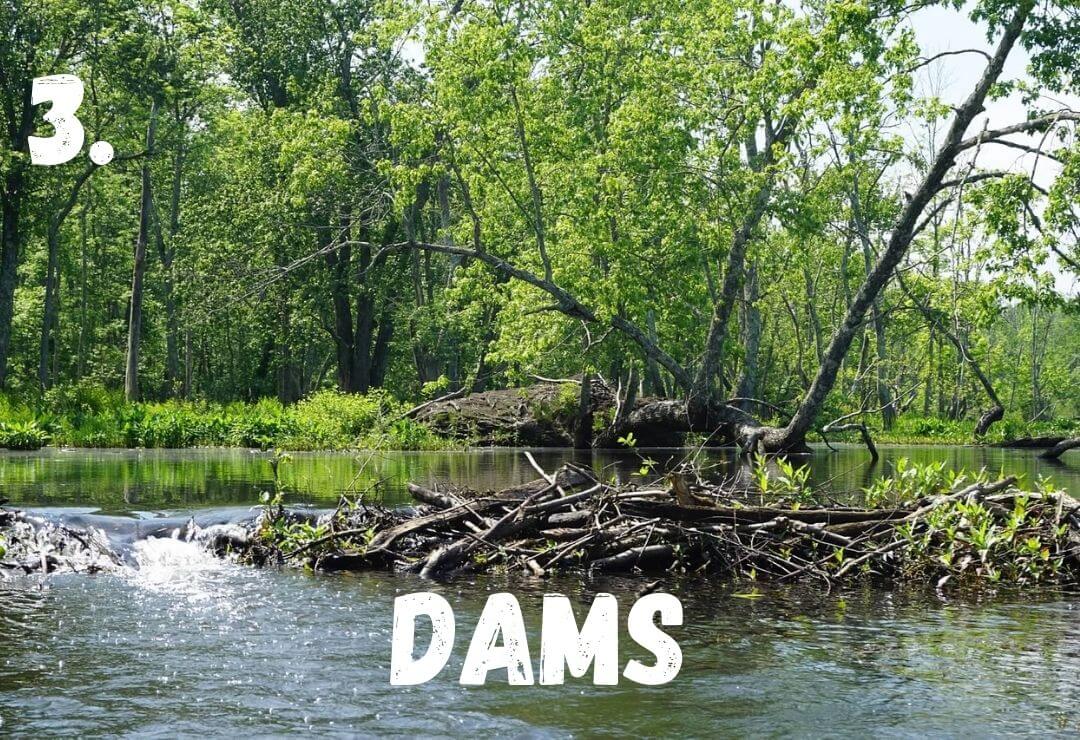
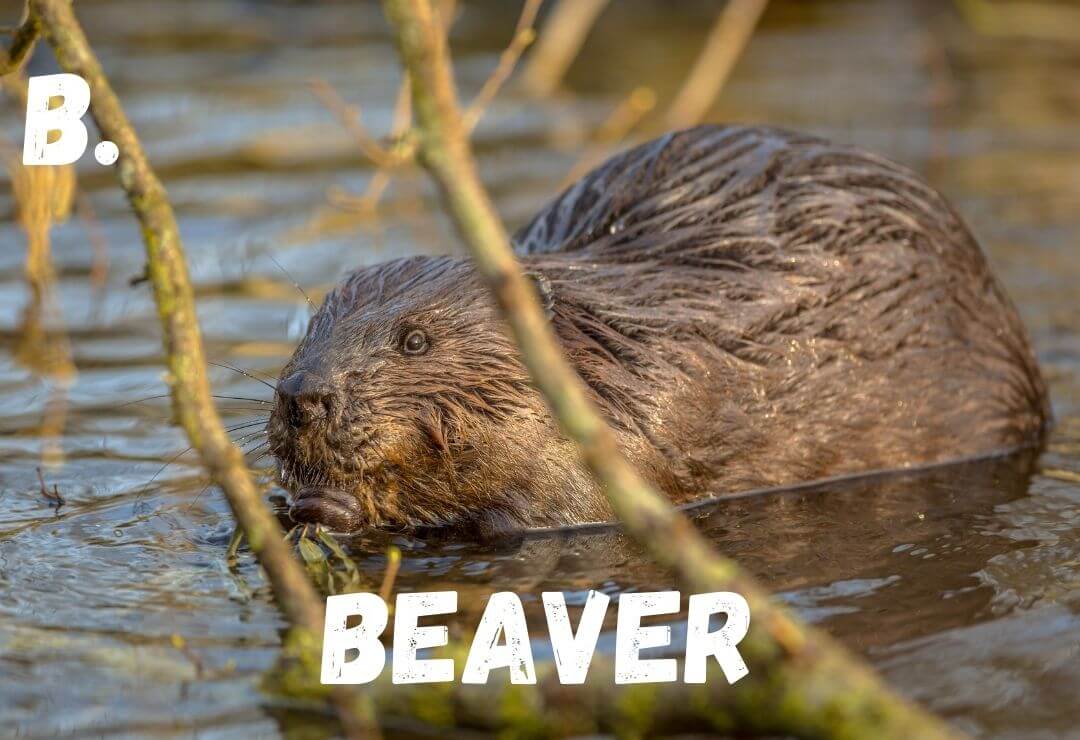
B - Beaver
Beavers build dams that stop water flow and create ponds. These dams help filter the water while the ponds create a new ecosystem for other animals to use!
Challenge #2
Animals need many resources to survive. They need food, water, shelter, and oxygen, and sometimes they need to engineer their ecosystem to get those resources!
For challenge #2, become an ecosystem engineer! Pretend you live in the forest ecosystem shown in this photo. Draw a picture showing how you would engineer this ecosystem to help you get the resources you need! Think about how you would collect food, where you would find water, and how you would have to change the ecosystem to survive.
DAY 3
Environmental Indicator
In simplest terms, environmental indicators are things that measure or represent the health of an ecosystem.
There are many abiotic (non-living) environmental indicators. We may be able to tell the health of an aquatic ecosystem by measuring water temperature or carbon dioxide concentration. We may be able to tell the health of a forest ecosystem by measuring soil quality or precipitation patterns.
Environmental indicators can also be biotic (living), and that's what we are going to focus on! These organisms may also be called indicator species. The presence or absence of some plants or animals can tell us if an ecosystem is healthy or not. Check out these examples!
Amphibians
Amphibians have permeable skin, meaning water and other nutrients can pass through it. This makes them vulnerable to toxins in the environment, which can also be absorbed through their skin. When the amphibian population in an ecosystem shrinks or disappears, it represents poor ecosystem health.
Spotted Owl
Northern spotted owls are a key indicator species in old-growth forests of the northwestern United States. For spotted owls to flourish, there needs to be a large diversity of plants and animals. They rely on old-growth trees and other birds for their nesting sites and feed on a wide array of small animals. When spotted owls are present, it represents a healthy forest.
Platypus
Platypuses are one of the most unique mammals in the world. They feed on small invertebrates, like shrimp and other crustaceans, in streams and ponds of Australia. They are known to be a resilient species and are usually one of the first animals to come back to a restored ecosystem. Their return represents successful conservation work!
Interpreting the Ecosystem
In the scenarios below, what can you interpret about the health of the ecosystem based on the environmental indicator? Click the drop-down arrow to check your work.
- Each year, many frogs lay their eggs in the shallow parts of the pond. This year, there are hardly any eggs.
- Answer
The frogs are indicating that this ecosystem is not healthy.
Because frogs and their eggs are highly susceptible to toxins, they avoid areas that are polluted.
2. Platypuses have not been seen in this river in nearly a decade. This year, a platypus has made its home here!
- Answer
The platypus is indicating that this ecosystem is healthy!
Platypuses are often one of the first animals to return to a restored ecosystem. It lets biologists know that their conservation efforts are working.
3. In recent years, storks have stopped gathering at their favorite fish-eating spot.
- Answer
The storks are indicating that this ecosystem is not healthy.
Storks normally gather in large groups where there is plentiful food. Their disappearance must mean the water quality is not healthy enough to support fish and aquatic invertebrates.
4. Mosses (which can pick up air pollutant particles) have become more common in the forest.
- Answer
The moss is indicating that this ecosystem is
healthy!
Moss often disappears from an area when there are high levels of air pollutants. Moss returning to the area must mean that the amount of pollutants in the air has dropped!
5. Corals (which are sensitive to water pollution) have started to die off and turn white.
- Answer
The coral is indicating that this ecosystem is not healthy.
Coral bleaching occurs when water temperatures get too warm for them to survive. When they die, the corals turn white and tell us that the water is no longer suitable.
6. Biologists have been cleaning up a nearby stream. Salamanders have started to return!
- Answer
The salamanders are indicating that this ecosystem is healthy!
Salamanders are a type of amphibian, meaning their skin is permeable and they are threatened by pollution. Their return to an area means there are fewer pollutants in the stream!
Challenge #3
Scientists have been studying a nearby forest for many years. At first, the forest was home to a wide variety of plants and animals, including spotted owls! However, over the past couple of years, scientists have noticed that the forest is being logged for paper production, and spotted owls have become scarce, indicating that the forest is in trouble.
For challenge #3, devise a plan to save this forest! Pretend you are one of the scientists and it is your job to come up with ideas on how to restore the forest. Identify at least two ideas that could benefit the ecosystem. These ideas can involve ways to reduce logging, how to bring species diversity back, how to monitor forest health, or any other ways you could help the forest!
DAY 4
Apex Predators
Apex predators are the top predator in the food chain! They are large, powerful carnivores that have no natural predators.
Most ecosystems have an apex predator at the end of their food web that helps to control populations of herbivores and even smaller carnivores. Apex predators are often considered keystone species because of their importance in their ecosystems.
If we removed the apex predator from their ecosystem, a trophic cascade would occur. A trophic cascade is a domino effect that occurs when we add or remove a predator or prey species from its ecosystem. If we added or removed an apex predator, every animal in the food web would be impacted.
Check it out! When there are too many predators, they overconsume grazers and the vegetation grows unchecked. When the population of predators is too small, populations of grazers grow unchecked and overgraze the landscape. We saw an example of this in "How Wolves Change Rivers."
Apex Adventure
Identify which animal is the apex predator in each particular ecosystem! Click the drop-down arrow to check your work.
- 3. Tundra Ecosystem
Polar bear.
Polar bears are powerful predators. As adults, they have no natural predators, unlike the arctic hare.
- 5. Temperate Woodland Ecosystem
Wolf.
While foxes are predators, they are not at the top of the food chain like wolves are. Foxes can be preyed on by wolves, large birds, or even mountain lions, depending on the region.
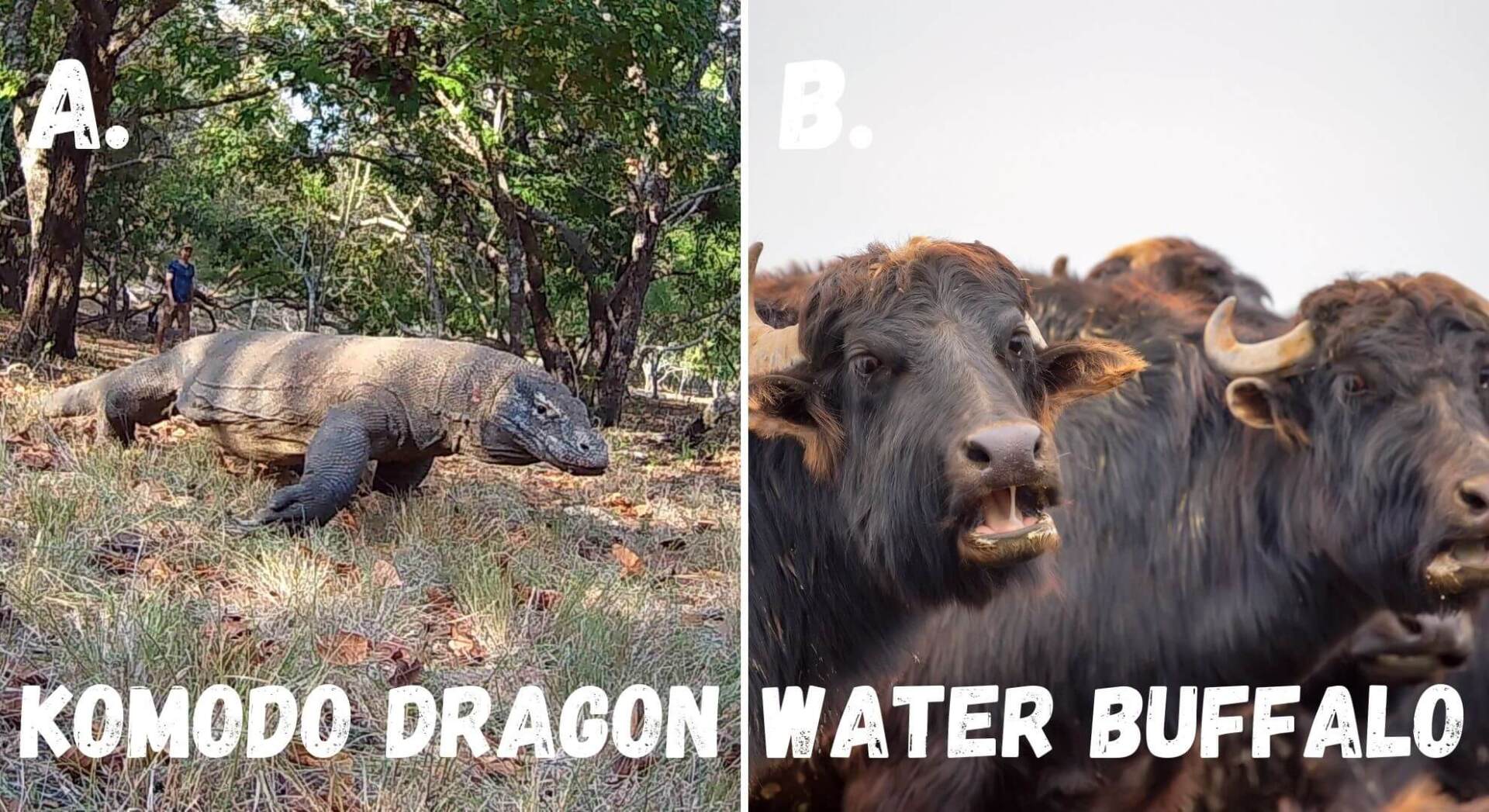
- 7. Savanna Forest Ecosystem
Komodo dragons.
Komodo dragons are the world's largest lizard! They are the apex predators on their islands and commonly feed on water buffaloes.
Challenge #4
The African savanna is filled with predators and prey that all work to keep the ecosystem balanced. The video below describes many of the incredible animals that inhabit the savanna.
For challenge #4, we're going to build a food chain! Using at least THREE species described in the video, build a food chain that includes an apex predator! Your food chain will start with a plant (grass, trees, etc.) followed by your three animal species. You may have to do a little research to see what the different animals eat!
Too easy?! Select at least SIX animals described below and build a food web.
DAY 5
Some Organisms Have it All!
All of the plants and animals described above have one major characteristic in common: without them, ecosystems would change drastically. Scientists are able to focus on the important organisms to better conserve ecosystems!
Without keystone species, a domino effect would cause the ecosystem to collapse. Keystone species can be the smallest prey species, the largest predator, or anywhere in between!
Without ecosystem engineers, the landscape itself would be altered and species that depend on their engineering would suffer.
Without indicator species, it would be more challenging for scientists to conserve ecosystems and other, more tolerant species would slowly become less healthy.
Without apex predators, trophic cascades would cause populations of other species to spike or drop dramatically. They are the top predator in the food chain!
Apex predators are often considered keystone species because of the domino effect that would occur if they were removed. Ecosystem engineers are also frequently considered keystone species because of their huge impact in constructing the ecosystem. Indicator species may also be apex predators because a healthy population of predators indicates wide species diversity in the ecosystem.
Identifying Ecosystem Roles
For each organism below, identify if they are keystone species, ecosystem engineers, indicator species, or apex predators. Remember, some organisms can play several different roles!
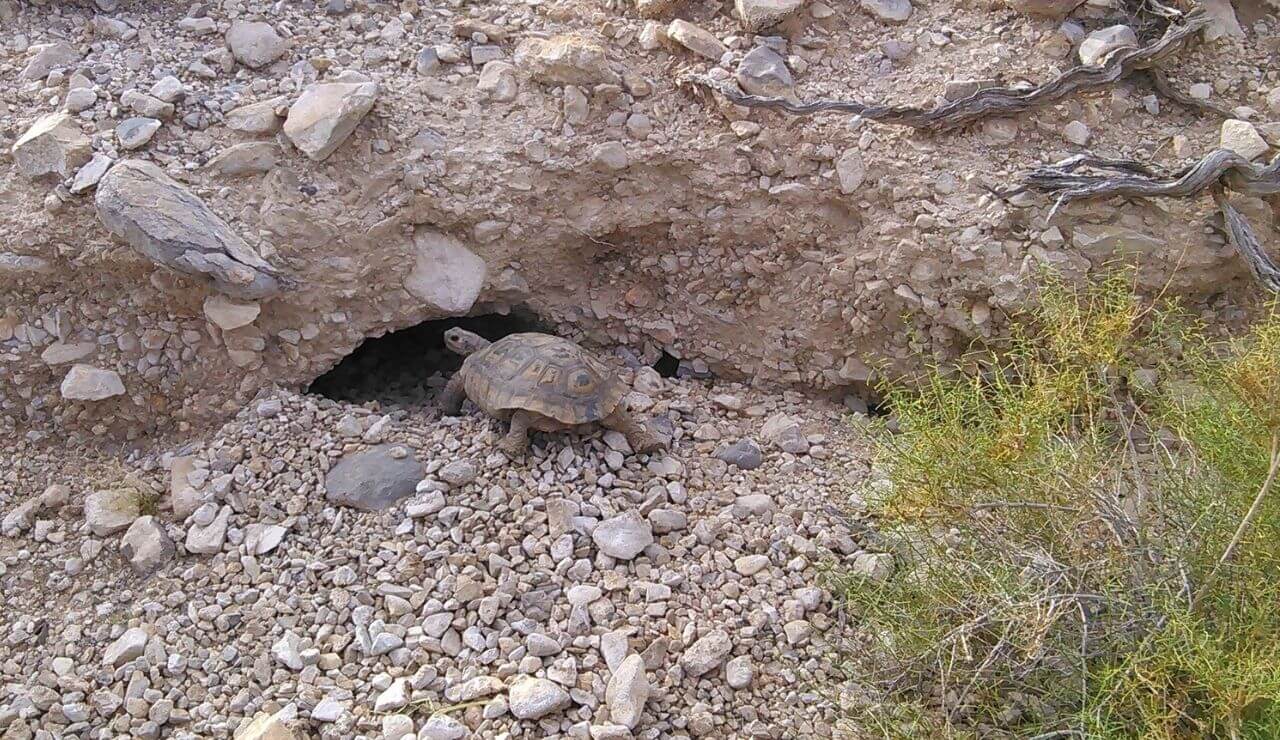
- 1. The burrowing DESERT TORTOISE has higher populations in habitats without people.
Desert tortoises are ecosystem engineers and indicator species.
Tortoises modify the ecosystem by building extensive burrow systems that other animals can use. They also indicate the ecosystem's health because of their sensitivity to human development, disease, and overgrazing.
- 2. TERMITES build huge mounds throughout the landscape where the soil is healthy.
Termites are ecosystem engineers and indicator species.
They modify the landscape by building giant mounds and only thrive in areas with healthy soil.
- 3. JAGUARS are only found in diverse ecosystems and help keep populations of grazers in check.
Jaguars are apex predators, keystone species, and indicator species.
Jaguars are powerful predators and play an important role in keeping grazer populations in check. They have no natural predators in their ecosystem. Their presence means that there are healthy populations of prey species and the ecosystem is healthy.
- 4. GIANT KELP creates habitats for many aquatic species and supports the whole ecosystem.
Giant kelp is an ecosystem engineer and a keystone species.
The presence of giant kelp maintains a diverse ecosystem by giving other species places to live and hide. They are a keystone species because, without them, the ecosystem would change from a dense, protected area to an open ocean.
- 5. MARTIAL EAGLES are huge and powerful predators that feed heavily on small animals.
Martial eagles are apex predators and indicator species.
Martial eagles have no natural predators in their African ecosystem and are only found in undisturbed areas where there are plentiful prey species, which indicates a healthy ecosystem.
- 6. HUMANS build cities and farms and heavily impact many ecosystems.
Humans are ecosystem engineers and keystone species.
Humans have modified, destroyed, and created many different ecosystems through building communities and farms. If we removed the human population, ecosystems would change dramatically. You may argue that humans are apex predators, however, without our tools and weapons, we could easily be prey to some species!
Challenge #5
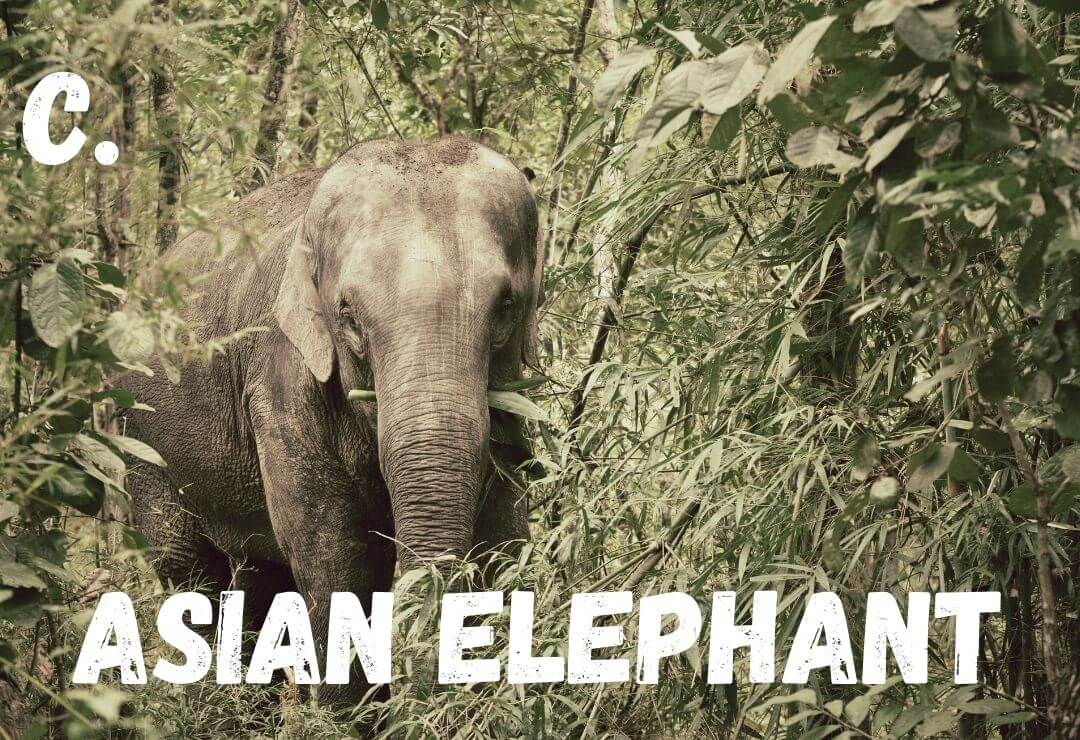
Elephants are some of the world's favorite animals. Not only are they beautiful and majestic, but they also play huge roles in their ecosystem! Elephants are often considered keystone species, ecosystem engineers, AND indicator species! Watch the video below to get a better understanding.
For your
5th and final challenge, tell a story about how the ecosystem would change if we removed Asian elephants from the perspective of a smaller animal in the forest. In 1-2 paragraphs, describe how you would be affected by the elephant's disappearance and what would happen to the ecosystem around you!
Glossary
Abiotic
The non-living parts of an environment, like the temperature, rainfall, rocks, or dirt.
Adaptation
The process by which a species becomes more fit for its environment over the course of several generations. It is a result of natural selection.
Apex Predator
A carnivore at the top of the food chain that has no natural predators.
Biotic
The living parts of an ecosystem, like the plants and animals.
Carnivore
An animal that eats other animals.
Commensalism
A symbiotic relationship between two species where one species benefits and the other is unaffected.
Deforestation
The process of removing trees by cutting them down or burning them to harvest their resources or make room for something else.
Ecosystem
A specific region made up of groups of living organisms that interact with each other and the non-living components of the environment.
Ecosystem Engineer
Organisms that significantly modify, maintain, create, or destroy an ecosystem.
Environmental Indicator
Organisms whose presence or absence represents the health of an ecosystem. They are sometimes called indicator species.
Food Chain
Tool used by scientists to show how energy flows throughout a single pathway in an ecosystem.
Food Web
Tool used by scientists to show how energy flows throughout many pathways in an ecosystem.
Grazers
Herbivores that feed heavily on grasses and other ground cover.
Herbivore
An animal that eats plants.
Keystone Species
Plants, animals, or fungi that have an incredibly large impact on their ecosystem regardless of population size.
Omnivore
An animal that eats both plants and animals.
Pollinator
An organism that moves pollen between flowers and fertilizes plants. Bees and hummingbirds are commonly known pollinators.
Predator
An animal that hunts and eats other animals. They are carnivores.
Prey
An animal that is hunted and eaten by another animal.
Looking for more amazing lessons?
Check out our EdZOOcating Adventures using the link below!
Sign Up for our Newsletter
Stay up to date with new adventures, classes, deals, and more!
MENU
EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES
All Rights Reserved | Edzoocating.com